CHAPTER 5
AN INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS
TEST YOURSELF
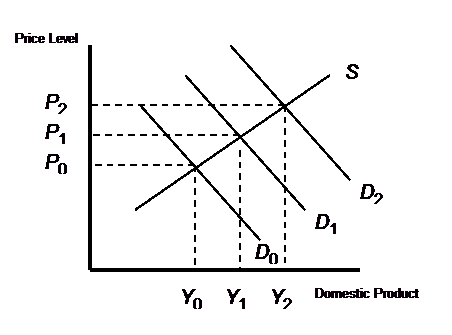
2. Figure 1 shows an economy with a fixed aggregate supply curve, and an aggregate demand curve that shifts out each year, from D0 to D1 to D2, etc. Prices would rise continuously, from P0 to P1 to P2, and production would increase, from Y0 to Y1 to Y2.
Figure 1

DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
3. There are many reasons why the GDP is not an accurate measure of the nation’s well-being. The GDP excludes most goods and services that are not sold in the market, some of which (like child care in the home) are very valuable. It omits consideration of the value of leisure. While it adds up the money value of “goods,” it makes no subtraction for “bads,” like pollution and natural disasters. It takes no account of income distribution—and presumably our assessment of a nation’s well being would depend in part upon whether the goods and services are concentrated among a few people, or are widely distributed.